Core concepts
These core concepts underpin the Australian Curriculum: Digital Technologies V9.0.
The core concepts specific to Digital Technologies are:
Core concepts
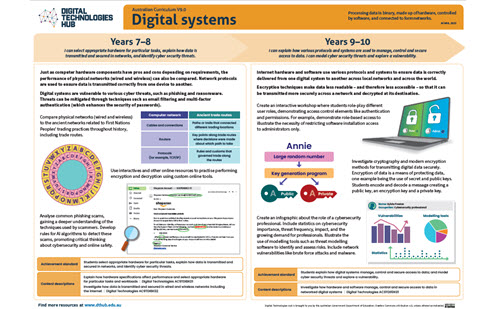
Digital systems is a core concept that is introduced in Foundation year and continues through to Year band 9-10.
This focuses on the components of digital systems, hardware and software and networks including the internet and the way in which data is transmitted.
ACARA defines Digital systems as ‘Processing data in binary, made up of hardware, controlled by software, and connected to form networks.’
View the poster for your Year band for an explanation of the concept with relevant examples and ‘I can’ statements.
The posters are designed to assist in the interpretation and support the implementation of the Australian Curriculum V9.
Download and use these A3 posters in planning sessions and use them to view the progression of this core concept across Year bands.
|
|
|
|
Download all posters here.
View this curated topic on Digital Systems.
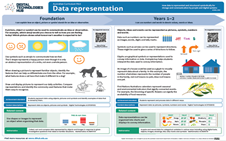
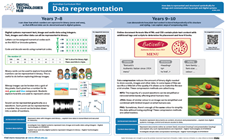
Data representation is a core concept that is introduced in Foundation year and continues through to Year band 9-10.
ACARA defines Data representation as ‘How data is represented and structured symbolically for storage and communication by people and digital systems’.
View the poster for your Year band for an explanation of the concept with relevant examples and ‘I can’ statements. The QR code provides a link to relevant resources.
The posters are designed to assist in the interpretation and support the implementation of the Australian Curriculum V9.
Download and use these A3 posters in planning sessions and use them to view the progression of this core concept across Year bands.
|
|
|
|
Download all posters here.
View this curated topic on Data representation.
Data acquisition is a core concept of Digital Technologies curriculum. Data acquisition includes a focus on collecting data via survey and questionnaire and using existing datasets such as those available in online repositories.
ACARA defines Data acquisition as ‘Numerical, categorical or structured values acquired or calculated to create information’.
A further definition is ‘Explore the properties of data, how it is acquired and interpreted using a range of digital systems and peripherals and analyse data when creating information’ ACARA 2022.
In Years F-6 students acquiring data is covered in Mathematics: Statistics starting in Foundation year. At these year levels, acquiring data is covered by the content descriptions in Mathematics with the intention of integrating with Digital Technologies, for examples refer to Data representation Years 1-2 and Years 3-6. For examples of lessons with a statistics focus refer to the Maths Hub Planning tool and select your year level.
In Years 7-10 acquiring data is covered in both Mathematics: Statistics and Digital Technologies Acquiring, analysing and visualising data.
At these year bands, Acquiring, managing and analysing data relates to tasks that provide opportunity for students to acquire, store and validate data from a range of sources using software, including spreadsheets and databases.
This infographic is designed to assist in the interpretation of the Australian Curriculum V9.
Download and use this A3 poster in planning sessions and use it to view the progression of this core concept across Years 7-10.
Download the Acquiring, analysing and visualising data posters across Year bands.
|
Acquiring, analysing and visualising data poster (Years 7–8) |
Acquiring, analysing and visualising data poster (Years 9–10) |
Download all posters here.
Data interpretation is a core concept of Digital Technologies curriculum.
ACARA defines Data interpretation as ‘Extracting meaning from data'.
A further definition is ‘Explore the properties of data, how it is acquired and interpreted using a range of digital systems and peripherals and analyse data when creating information’ ACARA 2022.
In Years F-6 students data interpretation is covered in Mathematics: Statistics starting in Foundation year. At these year levels, data interpretation is covered by the content descriptions in Mathematics with the intention of integrating with Digital Technologies, for examples refer to Data representation Years 1-2 and Years 3-6. For examples of lessons with a statistics focus refer to the Maths Hub Planning tool and select your year level.
In Years 7-10 data interpretation is covered in both Mathematics: Statistics and Digital Technologies Acquiring, analysing and visualising data.
At these year bands, Acquiring, analysing and visualising data relates to tasks that provide opportunity for students to acquire, store and validate data from a range of sources using software, including spreadsheets and databases.
This infographic is designed to assist in the interpretation of the Australian Curriculum V9.
Download and use this A3 poster in planning sessions and use it to view the progression of this core concept across Years 7-10.
Download the Acquiring, analysing and visualising data posters across Year bands.
|
Acquiring, analysing and visualising data poster (Years 7–8) |
Acquiring, analysing and visualising data poster (Years 9–10) |
Download all posters here.
Abstraction is a core concept in Digital Technologies, however it does not explicitly appear in content descriptions.
ACARA defines abstraction as 'reducing complexity by hiding details so that the main idea, problem or solution can be defined and focus can be on the manageable number of aspects'.
ACARA defines specification as 'defining a problem precisely and clearly, identifying the requirements, and breaking the problem into manageable pieces'.
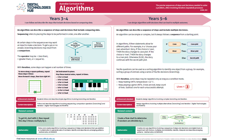
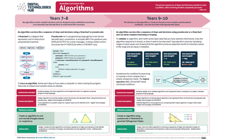
Algorithms is a core concept that is introduced in Year 1 and continues through to Year band 9-10.
ACARA defines Algorithms as ‘The precise sequences of steps and decisions needed to solve a problem, often involving iterative (repeated) processes.’
View the poster for your Year band for an explanation of the concept with relevant examples and ‘I can’ statements. The QR code provides a link to relevant resources.
The first poster includes approaches used to teach students about algorithms from Years 1-10.
The posters are designed to assist in the interpretation and support the implementation of the Australian Curriculum V9.
Download and use these A3 posters in planning sessions and use them to view the progression of this core concept across Year bands.
|
|
|
|
Download all posters here.
View this curated topic on Algorithms.
Implementation (programming) is a core concept that is introduced in Year 3 and continues through to Year band 9-10.
ACARA defines implementation as ‘the automation of an algorithm, typically by writing a computer program or using appropriate software.’
View the poster for your Year band for an explanation of the concept with relevant examples and ‘I can’ statements. The QR code provides a link to relevant resources. Note for Years F-2 relevant related content is suggested.
The first poster includes approaches used to teach students about programming from Years 3-10.
The posters are designed to assist in the interpretation and support the implementation of the Australian Curriculum V9.
Download and use these A3 posters in planning sessions and use them to view the progression of this core concept across Year bands.
Download all posters here.
View these curated topics on Visual programming and General purpose programming.
Privacy and security is a core concept that is introduced in Foundation year and continues through to Year band 9-10.
ACARA defines privacy and security as 'The protection of data when it is stored or transmitted through digital systems'.
Privacy includes recognising the risks that are faced online and the mitigation strategies involved in managing them.
Security covers the development of appropriate technical, social, cognitive, communicative and decision-making skills to address online and network security risks. It includes data security, and ethical and legal considerations when working with and designing digital systems.
View the poster for your Year band for an explanation of the concept with relevant examples and ‘I can’ statements.
The posters are designed to assist in the interpretation and support the implementation of the Australian Curriculum V9.
Download and use these A3 posters in planning sessions and use them to view the progression of this core concept across Year bands.
|
|
|
|
Download all posters here.
Overarching concepts
This helps people to organise data logically by breaking down problems into parts; defining abstract concepts; and designing and using algorithms, patterns and models.
View curated topic on Computational thinking.
This helps people to think holistically about the interactions and interconnections that shape the behaviour of systems.
View curated topic on Systems thinking.
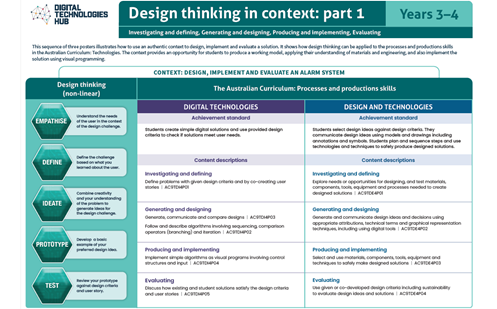
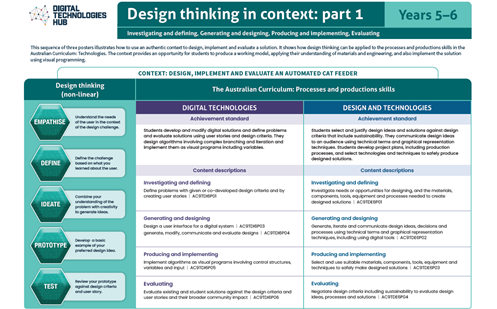
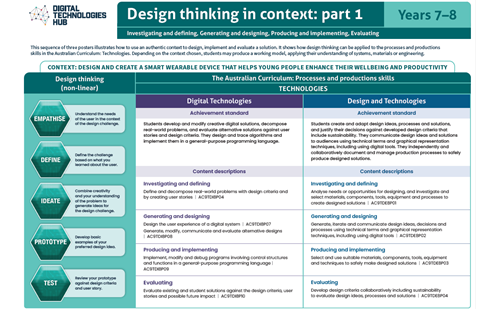
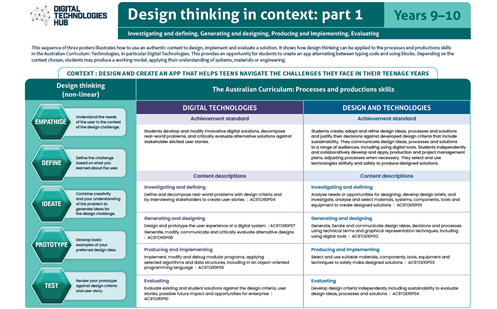
This helps people to empathise and understand needs, opportunities and problems; generate, iterate and represent innovative, user-centred ideas; and analyse and evaluate those ideas. View ACARA’s poster on Design thinking.
To get an understanding of how design thinking can be applied to developing design ideas, view our poster series on Design thinking in context.
View the poster for your Year band for an explanation of the concept with relevant examples. The posters are designed to assist in the interpretation and support the implementation of the Australian Curriculum V9.
Download and use these A3 posters in planning sessions and use them to view the progression of this core concept across Year bands.
|
|
|
Download all posters here.
View curated topic on Design thinking.