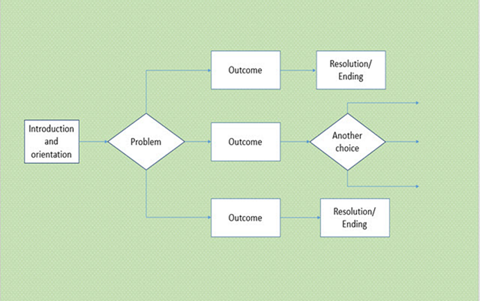
Plan a 'choose your own adventure' story
Students create a storyboard to plan a ‘choose your own adventure' story, where the reader is provided with a number of decisions that lead to alternative endings.
Additional details
| Year band(s) | 3-4 |
|---|---|
| Content type | Lesson ideas |
| Format | Web page |
| Core and overarching concepts | Algorithms |
| Australian Curriculum Digital Technologies code(s) |
AC9TDI4P02
Follow and describe algorithms involving sequencing, comparison operators (branching) and iteration |
| Technologies & Programming Languages | Scratch |
| Keywords | Branching, Algorithms, Choose your own adventure, Storyboard, Inclusive education, disability, disabilities |
| Integrated, cross-curriculum, special needs | English, Digital Literacy, Inclusive education |
| Organisation | ESA |
| Copyright | Creative Commons Attribution 4.0, unless otherwise indicated. |
Related resources
-

Classroom ideas: Choose your own adventure (Years 3-6)
In Digital Technologies, students from Year 3 onwards should be planning and implementing projects that include branching (decision-making). Creating a ‘choose your own adventure’ story is an excellent way for students to design and implement a project that makes use of branching.
-
Visual programming with Scratch (Years 3-6)
This resource comprises a collection of sample activities that incorporate visual programming (Scratch) into teaching and learning programs.
-

Robots, data and computational thinking (Years 2-4)
This classroom resource comprises four worksheets to accompany a lesson on data and computational thinking. These materials are designed for teachers to use simple line-following robots (Ozobots) to engage students in the computational thinking process and working with data.
-

Computing at School: Resources
Browse the curriculum resources which are tried and classroom tested resources submitted by primary teachers to support Computing for early to middle primary school. Requires free registration.
-

Introduction to Micro:bit Project Collection
A collection of projects that can be used as an introduction to using micro:bits.
-

Bee Bot Balloon Pop
During this lesson, students will be required to consider the functions of the Bee-Bot and how a user can interact with this device.
-

Water Water everywhere!
In this lesson, students are presented with the challenging problem of measuring a volume of water using containers that are not the exact measurement size.
-

Automated soil moisture sensor
The soil moisture sensor project integrates science understandings and computational thinking to solve a problem about sustainable watering practices.